- Country Profile
- Student Life
- Education
- Requirements
- Costs
- FAQs
- prev
- next
Intro
Introduction to USA for International Students

The USA is considered the most attractive study destination in the world, with a yearly average of over one million international students. However, some may wonder how the USA manages to maintain its appeal despite having a relatively high cost of living and tuition. Simply, The United States has it all for international students seeking the perfect study destination - from prestigious universities with rigorous admission standards to community colleges with flexible eligibility criteria, offering a diverse range of study opportunities for students of all academic backgrounds.
According to the QS World University Rankings 2024, Study in USA among the most highly regarded options, with 10 universities ranked in the top 20 globally, with one of them being in first place and two in the top five. This just illustrates how well-respected universities in the USA are, and shows that they can provide students with excellent education and research opportunities.
The USA also offers an array of experiences for its international students, ranging from cosmopolitan cities like New York to small towns perfect for rural living. There is something in the US suitable for everyone, and it is easy to find a college or university that fits individual preferences with no compromise.
No matter what you study in the USA, the quality of American education is guaranteed to be exceptional and world-class. With renowned professors, top-notch facilities, and cutting-edge research opportunities, you can rest assured that your educational experience will be nothing short of extraordinary.
Why do international students study in USA?
International students choose to study in the USA for various reasons, including the international exposure and diverse learning environment. According to the Global Student Satisfaction Report 2023, many students appreciate the international atmosphere, the presence of students from different countries, and the opportunity for exchange programs. The report also highlights that the USA has the highest overall student satisfaction score among the top global study destinations, with a score of 4.27 out of 5. Additionally, universities in the USA have a strong hold on dimensions such as admissions processing, student-teacher interaction, and career development, with high satisfaction ratings. The USA offers a vibrant social life, diverse entertainment options, and a well-developed healthcare system, which are all factors that attract international students. Below are the top reasons for international students to study in USA according to the report,
- International Exposure: Students appreciate the international atmosphere, presence of students from different countries, and opportunities for exchange programs.
- Inclusivity: Many students feel included and supported on campus, although some face challenges integrating with local students or communities.
- Support for International Students: Universities provide academic support, assistance with adapting to a new environment, mentorship programs, and social/cultural activities.
- Challenges Faced: Some students face difficulties adjusting to a new country, discrimination, or financial constraints. This is minimal in the USA.
- Engage with Employers: Universities should invite top employers to discuss desired skills and provide career development opportunities.
- Practical Skills & Real-World Relevance: Students value practical exercises, internships, and industry exposure to bridge the gap between theory and application.
- Student Diversity: Universities should create an inclusive environment, promote a diverse syllabus, and encourage participation from all students.
- Career Development: Students appreciate internships, job opportunities, and connections with industry professionals.
- Student-Teacher Interactions: Positive relationships with teachers enhance the student experience.
- Quality of Student Life: Universities should offer services beyond learning, support personal development, and align with students’ values.
- Admission Process: Transparency, quick responses, ease of application, and updated information are important for a positive experience.
- Regional Differences: Student satisfaction in the Americas is generally high, while EMEA and APAC regions have slightly lower ratings.
Quality of American Education

The United States is home to some of the top-ranked universities in the world, Study in USA offers access to some of the most prestigious universities globally. According to the QS World University Rankings 2024, four of the top ten universities globally are located in the USA. These prestigious institutions include the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Harvard University, Stanford University, and the University of California, Berkeley (UCB). Additionally, the American Ivy League, consisting of eight renowned colleges such as Cornell University, Columbia University, Princeton University, and Yale University, further adds to the country’s academic reputation. These top-ranked universities in the USA provide a wide range of courses and programs, equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary for successful careers. Studying at these institutions not only offers a high-quality education but also enhances a student’s career profile upon graduation.
Top Study Majors for International Students in the USA
When it comes to top study majors for international students in the USA, several fields stand out. Business and Management programs are highly sought after, given the global significance of the USA in commerce. Computer Science and Information Technology programs are also popular, as the USA is a hub for technological innovation. Engineering programs attract students with their focus on innovation and hands-on experience. Medicine and Health Sciences programs provide access to advanced healthcare systems and state-of-the-art facilities. Social Sciences programs foster critical thinking and a deep understanding of society. Art and Design programs celebrate individual expression and innovation. These study majors offer international students a wide range of opportunities for academic and career growth in the USA.
Also check: Study Engineering at Embry Riddle Aeronautical University in Florida
American Economy and Technology
The United States of America is a global powerhouse when it comes to both economic and technological advancements. known as the land of opportunity, It stands as one of the largest and most influential economies in the world, driving innovation and shaping industries across various sectors.
The USA boasts the world's largest economy, with a GDP of over $21 trillion. Its sheer size and diverse range of industries contribute to its economic strength. From finance to technology, manufacturing to entertainment, the USA offers a wide range of opportunities for growth and development, and it has become a leader in many fields.
The United States is also home to some of the most prestigious technology companies in the world, with Silicon Valley being one of the most notable locations in the country. Companies like Apple, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Intel, and Facebook all have their headquarters in Silicon Valley and are constantly driving technological innovation and progress. For students interested in a career related to these companies or any other related field, a degree from the USA is sure to open up many doors.
Therefore, for any international student looking for a top-notch education with plenty of career opportunities, studying in the United States can be an exciting and life-changing experience. With its diverse culture, prestigious universities, and economic and technological powerhouses, the USA is an ideal destination for those seeking to further their education.
Job Opportunities for International Students in USA

Studying in the United States as an international student can be an exciting and enriching experience. Apart from the quality of education provided by renowned universities, the USA also offers various job opportunities for international students. These opportunities not only help students gain valuable work experience but also provide them with the chance to earn money and support themselves financially during their studies, Many universities provide on-campus jobs for international students and there are also organizations like Optional Practical Training (OPT) that provide work authorization in certain areas of study for up to 12 months, In addition, many companies offer internships and other employment opportunities.
International students can work up to 20 hours a week while studying and full-time during their vacations. This can help them cover their living expenses, gain valuable work experience, and even get permanent residence status in the US after graduation.
Part-time jobs
Part-time jobs in the USA offer international students the opportunity to gain valuable work experience, earn income to help with the living cost, and enhance their skills while studying. International students with a student visa are eligible to work part-time in the USA, with a maximum of 20 hours per week during the academic term and up to 40 hours per week during school breaks. There are two types of student employment: on-campus and off-campus. On-campus employment refers to work within the college or university campus, while off-campus employment is affiliated with the institution. Off-campus jobs can fall under categories such as Optional Practical Training (OPT), Curricular Practical Training (CPT), Economic Hardship, and International Organizations. Popular part-time jobs for international students in the USA include library assistants, research assistants, and tutors, with average hourly salaries ranging from $12 to $17. While you still can find work related to your field of study, it is important to be familiar with the rules and regulations regarding part-time work and to explore opportunities that align with your interests and future career.
America's Cultural Diversity Enriches International Students

The USA is a nation of immigrants and proudly welcomes international students from across the globe. Students are introduced to a diverse and multicultural society, and they can learn about the different cultures that make up the country. This cultural diversity is one of the great attractions for international students in the USA.
The USA is also known for its diverse range of traditions, from widely celebrated American holidays such as Thanksgiving and Independence Day to regional customs like Mardi Gras and Cinco de Mayo. Students have the opportunity to experience these events firsthand and gain a deeper understanding of the country's culture.
One of the greatest strengths of cultural diversity in the USA is the opportunity for cross-cultural exchange. People from different backgrounds bring their unique perspectives, experiences, and ideas, which in turn fosters innovation, creativity, and problem-solving. This diversity of thought is invaluable in a globalized world where collaboration and understanding are essential.
Furthermore, cultural diversity in the USA promotes social cohesion and understanding. By living in a society with people from different backgrounds, individuals have the opportunity to learn about other cultures, challenge stereotypes, and foster empathy. This exposure to different perspectives helps to break down barriers and promotes inclusivity and equality.
Video
Location
-
United States
Why Study in USA?
- International Exposure
- Inclusivity
- Support for International Students
- Practical Skills & Real-World Relevance
- Student Diversity
- Career Development
- Quality of Student Life
- Regional Differences
Tuition at public schools ranges from $3,000 to $10,000 per year.
Featured Institutions
Featured Programs
Student Life in the USA

International student life in the USA is an unparalleled experience that offers students from all over the world a chance to thrive academically and personally. The USA has established itself as a global hub for higher education, boasting prestigious universities and a diverse cultural landscape. This article will delve into the various aspects of international student life in the USA, including academic opportunities, cultural immersion, career development, financial considerations, and travel experiences.
The USA’s education system is known for its flexibility, allowing students to explore diverse subjects and tailor their academic journey to their interests and career aspirations. Beyond academics, international students in the USA have the opportunity to immerse themselves in a vibrant and multicultural environment. Campus life is enriched by a plethora of student organizations and clubs, providing avenues for cultural exchange, personal growth, and the formation of lifelong friendships. These extracurricular activities allow students to engage with their passions, develop leadership skills, and create a sense of belonging within the campus community.
Exploring the USA and its diverse landscapes and cities is an exciting part of the international student experience. From iconic cities like New York City and Los Angeles to picturesque destinations like San Francisco and Boston, students have the opportunity to travel and immerse themselves in American culture during breaks and vacations. This exposure to different regions and cultures broadens their horizons and enriches their overall experience.
Career development is another crucial aspect of the international student experience in the USA. Universities and colleges often offer comprehensive career services, including internships, job placement assistance, and networking opportunities. International students can gain valuable work experience through Optional Practical Training (OPT) programs, which allow them to work in their field of study for a specified period after graduation. This practical exposure enhances their employability and equips them with the skills necessary to succeed in the global job market.
It is important for international students to navigate the various aspects of their journey, seek support when needed, and make the most of the invaluable experiences that studying in the USA has to offer.
College Life Experience at US Universities

Campus life at US universities offers a vibrant and inclusive environment for international students to thrive academically, socially, and personally. One of the key aspects of campus life for international students is the opportunity to engage in cultural exchange. US universities are known for their diverse student populations, with students from different backgrounds and countries coming together to create a multicultural community . This diversity fosters an environment of understanding, tolerance, and appreciation for different cultures, allowing international students to share their own traditions and learn from others. Participating in cultural events, joining international student organizations, and attending multicultural festivals are just a few ways international students can immerse themselves in this rich cultural tapestry.
Students Clubs and Organizations
Extracurricular involvement is another integral part of campus life at US universities. American universities provide a wide range of clubs, student organizations, and extracurricular activities that cater to various interests and hobbies. Students can join academic clubs, sports teams, cultural organizations, and community service groups to meet like-minded individuals and develop new skills. Whether it’s joining a sports team, participating in a debate club, or becoming a member of a cultural or academic organization, international students have ample opportunities to pursue their hobbies, develop leadership skills, and make lifelong friendships. These extracurricular activities not only enhance the overall college experience but also provide valuable networking opportunities and avenues for personal growth.
Academic Support for International Students
US universities also prioritize academic support to ensure the success of their students. International students can benefit from a range of resources such as tutoring services, writing centers, and academic advising. These support systems are designed to help students excel in their coursework, develop effective study strategies, and navigate the academic requirements of their chosen programs. Additionally, professors and faculty members are often accessible and willing to provide guidance and mentorship to international students, fostering a supportive learning environment.
Social and Personal Development

The social life of students in the USA is vibrant and diverse, offering numerous opportunities for engagement and connection. Social events, such as parties, concerts of the world's biggest artists, and festivals, are also common on campuses, providing opportunities for students to socialize and have fun. Additionally, many universities organize orientation programs and social mixers to help international students integrate into the community and make friends. The USA’s cross-cultural experience fosters a sense of inclusivity and encourages students to embrace diversity and learn from different cultures. Overall, the social life of students in the USA offers a rich and dynamic experience that complements their academic journey.
Personal growth and development are integral components of campus life at US universities. The college experience offers a unique opportunity for international students to explore their interests, discover new passions, and develop essential life skills. Through involvement in student organizations, leadership roles, and community service, international students can enhance their communication skills, critical thinking abilities, and problem-solving capabilities. The diverse and inclusive campus environment encourages self-discovery, independence, and the development of a global perspective.
Extracurricular Activities at US Universities

Extracurricular activities play a significant role in the student experience in the USA, offering opportunities for personal growth, skill development, and social engagement. Universities in the USA provide a wide range of extracurricular activities, clubs, and organizations that cater to diverse interests and passions. Students can participate in academic clubs, such as debate teams or honor societies, to enhance their knowledge and skills in specific subjects. Sports teams and athletic clubs allow students to engage in physical activities and compete at various levels. Cultural and diversity clubs celebrate different cultures and provide platforms for students to share their traditions and experiences. Community service organizations offer opportunities for students to give back to society and make a positive impact. Examples of extracurricular activities in the USA include student government, music and theater groups, volunteer organizations, environmental clubs, and entrepreneurship clubs. These activities not only enrich the student experience but also provide valuable networking opportunities and contribute to personal and professional development.
Entertainment
Entertainment options in the USA for students are diverse and cater to various interests. The country offers a vibrant cultural scene with a wide range of entertainment opportunities. Students can explore museums, art galleries, and theaters to immerse themselves in the arts. Major cities in the USA host concerts of famous artists, music festivals, and live performances, providing students with the chance to experience a variety of music genres and performances. Sports enthusiasts can attend professional sports games or even participate in intramural sports leagues on campus. The USA is also known for its theme parks, such as Disneyland and Universal Studios, which offer thrilling experiences for students. Additionally, students can enjoy outdoor activities like hiking, skiing, and beach outings, depending on the region they are studying in. With its diverse entertainment options, the USA ensures that students have ample opportunities to relax, have fun, and make lasting memories during their time abroad.
Social Events
Universities and cities across the country host a wide range of social activities and events, providing opportunities for students to connect, have fun, and immerse themselves in American culture. These events can include music festivals, art exhibitions, cultural celebrations, sports games, and community gatherings. For example, cities like New York City, Los Angeles, and Chicago are known for their lively nightlife, offering clubs, bars, and live music venues for students to enjoy. Additionally, universities organize orientation programs, welcome parties, and campus-wide events to help students build friendships and create lasting memories. International students can also participate in student clubs and organizations that host social events catered to specific interests and hobbies. Overall, social events in the USA provide a vibrant and inclusive atmosphere for international students to engage with their peers and create a well-rounded student experience.
Tourism Activities
From iconic landmarks like the Statue of Liberty and the Grand Canyon to vibrant cities like New York City and Los Angeles, there is something for everyone. Students can visit famous national parks such as Yellowstone and Yosemite, go hiking in the Appalachian Mountains, or relax on the beautiful beaches of Florida or California. Cultural enthusiasts can explore museums, art galleries, and historical sites, immersing themselves in the rich history and heritage of the USA. Additionally, students can indulge in culinary adventures, trying diverse cuisines from different regions of the country. Whether it’s exploring natural landscapes, experiencing vibrant American city life, or delving into American culture, tourism activities in the USA provide international students with unforgettable life experiences and memories.
Weather and Geography
For international students Considering studying in the United States, understanding the weather and geography of the country is essential. The USA is known for its diverse climate and varied landscapes, offering a unique experience for students from around the world.
This diversity in weather and geography offers international students the opportunity to experience different environments and engage in various outdoor activities. For example, students can enjoy skiing in the Rocky Mountains, surfing in California, or hiking in national parks like Yellowstone or the Grand Canyon. Understanding the weather patterns and geographical features of the region where they choose to study is important for international students to prepare for the appropriate clothing, transportation, and recreational opportunities. It also allows them to fully immerse themselves in the natural beauty and outdoor adventures that the United States has to offer.
Adjusting to American Culture and Traditions

American culture is known for its diversity and openness, offering international students a chance to engage with a wide range of cultural practices and traditions . From attending local festivals and sports events to exploring historical landmarks and museums, international students have numerous opportunities to learn about American history, art, music, and cuisine. However, this natural comes with cultural barriers that international students need to overcome over the course of their program.
International students in the USA undergo cultural adjustment as they adapt to a new environment and navigate different cultural norms and practices. Universities provide support to help international students with cultural adjustment, including orientation programs, cultural events, and workshops. International students can also join clubs and organizations that celebrate their home country’s culture, providing a sense of familiarity and support. Engaging in campus life and participating in extracurricular activities can facilitate cultural adjustment by allowing international students to interact with American students and immerse themselves in the local culture. Universities may also offer courses or workshops on intercultural communication and cultural competency to help international students navigate cultural differences effectively. It is important to note that cultural adjustment is a personal and ongoing process, and universities provide resources and support to assist international students throughout their academic journey.
Cultural sensitivity and awareness are also important in overcoming communication barriers. Understanding cultural differences in communication styles, non-verbal cues, and social norms can help international students navigate conversations and interactions more effectively. Being open-minded, patient, and willing to learn from others can foster better communication and build stronger relationships.
Engaging in conversations with native English speakers and participating in language exchange programs can also be beneficial. This allows international students to practice their language skills in real-life situations and gain confidence in their communication abilities.
America's Culture and Traditions
The United States is one of the most culturally diverse countries in the world, with people from all walks of life living together in harmony. From bustling cities to peaceful rural towns, there is a wide variety of lifestyle options available to international students in the USA. As a student in the USA, you will have access to cultural experiences such as live music, theatre, art galleries, and festivals.
Celebrations and holidays play a vital role in American culture as well. From Thanksgiving, a holiday that commemorates the Pilgrims' first harvest in the New World, to Independence Day, which celebrates the country's freedom from British rule, Americans have a strong sense of national pride and come together to commemorate these occasions. Additionally, holidays like Christmas, Hanukkah, and Easter are celebrated by various religious and cultural groups, showcasing the diversity of traditions within the country.
Sports also hold a special place in American culture. Football, baseball, and basketball are widely popular, with millions of fans attending games and cheering for their favorite teams. Super Bowl Sunday, the championship game of the National Football League (NFL), has become an unofficial national holiday, complete with parties and gatherings.
Freedom of Speech
Freedom of speech is a fundamental right protected by the First Amendment of the United States Constitution. It is a pillar of democracy and a cornerstone of American society. The freedom to express one's thoughts, opinions, and beliefs without fear of censorship or retaliation is essential for the functioning of a free and open society.
The principle of freedom of speech also extends beyond the government's reach. Private companies and institutions, such as social media platforms and universities, often have their guidelines and policies regarding speech. While they are not bound by the First Amendment, these entities play a significant role in shaping the discourse and determining what is considered acceptable speech in their respective spaces.
American cuisine

One of the defining characteristics of American cuisine is its diversity. From coast to coast, you can find Plenty of regional dishes that showcase the distinct flavors and ingredients of different cultures. In the South, you'll find soulful dishes like fried chicken, collard greens, and cornbread, influenced by African, Native American, and European culinary traditions. Meanwhile, in New England, you'll discover seafood classics like clam chowder and lobster rolls, inspired by the region's proximity to the Atlantic Ocean.
American cuisine is also known for its love of comfort food. Indulgent dishes like hamburgers, macaroni and cheese, and apple pie have become iconic symbols of American food culture. These dishes are often associated with feelings of nostalgia and evoke a sense of home and familiarity.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on healthy and sustainable eating in America. Farm-to-table movements and a renewed interest in local, organic ingredients have influenced the way people approach food. As a result, farm-fresh salads, smoothie bowls, and plant-based alternatives have become more prevalent in American cuisine.
Submit an Inquiry
Video
Student Life in Numbers
- 57% of students gave 5 out of 5 on their satisfaction with life outside the university in USA according to the Global Student Satisfaction Report (2023).
Location
-
United States
The Education System in USA

The United States of America has a successful and organized educational system. In accordance with the American school system, the student must pass various levels of education through which he learns a lot of skills and methods of critical thinking and other requirements of the age to succeed. The American school system differs from the American university education system, where school education is a basic stage that everyone must pass successfully in 12 years or more or slightly less. And university education is not compulsory for all students except those who wish for a better and more sophisticated educational life.
The US education system may be organized very differently from the system in the home countries of international students. Reflected in a chart, it looks like this, complete with pathways between levels:
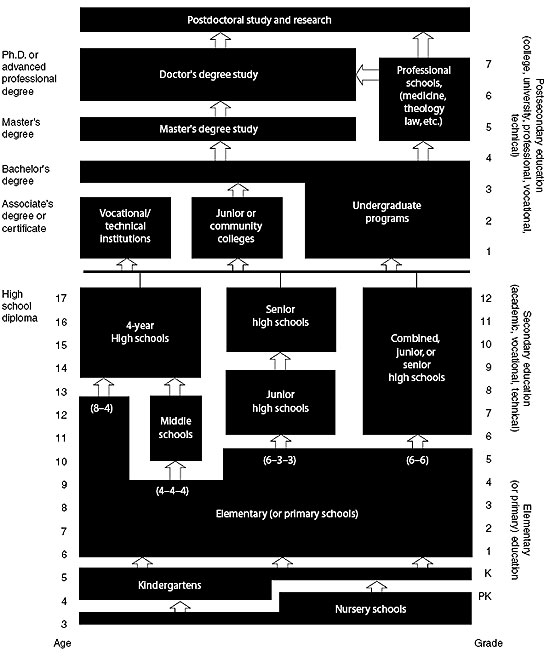
Pre-School and Kindergarten
American students begin either in preschool or kindergarten for one to three years before progressing to elementary (primary) school. In most states, the age at which a child must start school is six.
Most school districts offer a free year of kindergarten before the starting year; in most cases, children must be five years of age to enter kindergarten. If you are counseling a family planning to have a child under the age of six attending school in the US, make sure to ask the kindergarten schools under consideration about their cut-off birth dates for turning five, as this varies by school district.
Elementary (Primary) and High School (Secondary School)

Children attend elementary (primary) school for varying amounts of time. In most cases, they attend elementary until Grade 6. They then progress to one of the following: a junior high school for two years, a combined junior/senior high school (generally Grades 7–12), or a four-year high school. Please note that high schools can also be called secondary schools.
School-aged students in the US have the option of going to public schools (free) or to private schools (where they must pay tuition or be on scholarship). The vast majority (88%) attend public schools; nation-wide, 9% attend private schools, but this percentage is much higher in some regions and cities, and among Caucasian Americans. Three percent are home-schooled, in which case parents and/or caregivers provide education to children provided their practices meet the education laws of the state.
International students tend to attend K-12 private schools at a much higher rate than public schools, especially because public high school schools allow international students to study for only one year. Private schools have no such limit.
Graduating High School
There is no federally set national examination determining whether a student has successfully graduated high school in the US. However, 25 states require that students take a high-school exit examination for graduation, and three additional states have legislation that will see such exams required in the future.
Whether or not a national examination is used in assessment, American high schools issue high-school diplomas to students who have completed their curriculum.
Because different states and school districts determine what is taught in schools and how, the courses that must be completed to earn a high-school diploma will vary from one school and state to another.
American students normally graduate high school at age 17 or 18.
Post-secondary Education

The US offers a wide variety of higher education options for the diverse requirements and goals of domestic and international students. This variety encompasses:
- Types of institutions (e.g., private vs. public, academic vs. vocational, etc.)
- Length of programs (e.g., one year, two years, four years, etc.)
- Levels (e.g., associate, bachelor’s, master’s, post-graduate)
- Types of credential (e.g., non-degree, degree, micro-credential)
- Delivery models (e.g., online, hybrid, in-person)
- Tuition fees (from very affordable to extremely expensive)
- Location of institutions (e.g., urban vs. rural, west vs. east, etc.)
The US government notes that there are currently:
- 124,000 public and private schools in the US;
- Over 2,000 postsecondary non-degree career and technical schools (CTE);
- Over 4,000 degree-granting institutions of higher education.
They explain: “Of the higher education institutions, over 1,600 award associate degrees and some 2,400 award bachelor’s or higher degrees. Over 400 higher education institutions award research doctorates.”

Flexibility in the US Education System
International students may decide to begin at one type of institution (for example, a community college) and then move to another institution or level. Many higher education institutions have agreements that allow students to transfer credits achieved at a two-year institution to a degree program at a four-year institution. Students who choose to “mix and match” their study programs often do so because it can be more affordable. It is important to note that not all two-year programs lead seamlessly (through transfer credits) to four-year institutions. It is important to ask if there are agreements in place for international students interested in this kind of progression.
What is the difference between a “college” and a “university” in the US?
In the US, the terms “college” and “university” often – but not always – refer to the same kind of higher education institution (HEI), and as pathway provider Shorelight points out:
“Some are even called institutes (e.g., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, California Institute of Technology). Within larger universities in the United States, there are different colleges or schools that represent different academic areas of study (e.g., College of Engineering, School of Business).”
WENR concurs but adds a bit more clarification on characteristics a “university” must have but that a “college” may or may not offer:
“There are no nationally standardized definitions of “university” or “college,” and the name of an institution alone may not indicate exactly what type of institution it is. That said, a university, at minimum, offers bachelor’s programs and at least some master’s programs.”
The term “university” may also indicate that an HEI is relatively more research-intensive (e.g., with more postgraduate degrees) than other types of post-secondary education.
Types of American Higher Education Institutes (HEI)

For many years and especially in some countries, there has been a perception that the best universities in the US are in the Ivy league, a group of prestigious private institutions, or other large and well-known universities, but this is not always the case. Many less well-known colleges have excellent programs and can be the exact right fit for a student.
The American university system is diverse. Over 4,000 degree-granting institutions deliver a wide range of programs offering unique experiences for international students.
Part of the reason the higher education landscape is so diverse is that the federal government is not involved in recognizing educational institutions, programs or curriculums, or degrees or other qualifications. The US education system is “decentralized” as a result: state governments are responsible for overseeing the activities of higher education institutions.
Public Universities
Public universities (also known as State universities) receive at least some of their funding from the state government. Many belong to a state university system, which is a larger group of public universities spread throughout a US state that are connected in some ways through administrative functions but that operate separately from each other. Examples are State University of New York (SUNY), City University of New York (CUNY), and University of California (UC).
Most public universities are operated by the states and territories, usually as part of a state university system (which is a group of public universities supported by an individual state). Each state supports at least one state university and several support many more. California, for example, has an 11-campus University of California system, a 23-campus California State University system, and a 109-campus California Community Colleges System.
Local cities and counties may also support colleges and universities. The federal government manages only the five “service” academies (Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, and Merchant Marine) that are public; there is no “national” university.
It is very important to understand, therefore, that the use of the term “national” in a university names does not indicate federal support or stature. For example, National University of San Diego, California, is a private university. Similarly, the use of a state or city name does not automatically imply that an institution is public. Murray State University is a public university; the University of Pennsylvania, by contrast, is a private institution. Public universities are often larger and are often less expensive than private universities.
Private Universities
Private universities receive most of their revenue through students’ tuition fees, which are often higher than those charged by public universities. These institutions are often highly ranked and with very selective admissions requirements, include Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Harvard, and Yale. For more examples, please click here.
Private colleges and universities are those that do not receive their primary support from the government. Among these, some are secular while others have a religious affiliation (e.g., Roman Catholic, Judaism, etc.). In general, religiously affiliated institutions welcome students of all faiths, and religious courses are minimal or optional.
Private institutions are either non-profit or for-profit. For-profit institutions are often more focused on careers and technical education than academics. The University of Phoenix is a prominent example of a private, for-profit institution. Private universities are often more expensive than public ones, but they sometimes have more financial assistance set aside for international students. For-profit private universities and colleges. Unlike other types of university, for-profits operate as business ventures, aiming to make money for their shareholders as well as providing a good education for their students.
Liberal arts colleges offer mostly (though not exclusively) undergraduate courses focus on teaching undergraduate-level courses in the liberal arts and sciences (although some also offer graduate-level programs and more vocational subjects such as medicine, business administration or law).
Whether they are public or private, US colleges and universities vary in terms of what their overall focus is. Some emphasize a vocational, business, engineering, or technical curriculum; others emphasize a liberal arts curriculum. Many institutions combine some or all of the above.
Two-Years Community Colleges

Community colleges also known as two-year colleges and junior colleges are supported by public funding. According to The Department of Homeland Security, a community college can be defined as a “two-year school that provides affordable two-year post-secondary (associate degrees) educational programs as a pathway to a four-year degree.” However, this definition is expanding as these institutions are also being seen as very interesting alternatives to classic four-year colleges or institutions. Moreover, some community colleges are offering four-year bachelor’s degrees as well as two-year credentials. As College Board notes, community colleges “provide a separate type of learning that involves rigorous coursework and preparation for a future profession.”
There are currently about 1,000 community colleges in the US, of which the great majority are public and state funded. These two-year colleges enrolled 35% of all undergraduate students in the US in 2019/20 – the proportion is higher when the number of students in four-year bachelor programs offered by community colleges is counted.
The American Association of American Colleges (AACC) explains the role of community colleges like this: “Community colleges provide open access to post-secondary education, preparing students for transfer to four-year institutions, providing workforce development and skills training, and offering non-credit programs ranging from English as a second language to skills retraining to community enrichment programs or cultural activities.” In addition, some community colleges now offer four-year programs, including bachelor’s degrees.
Community colleges are very popular institutions for undergraduate studies in the US as in 2019/20 school year, approximately 11.8 million students were enrolled in community colleges, 9% of whom were international students. About 58% of community college programs are for credit, while 42% are non-credit. For international students, of course, non-credit programs will likely not be of interest unless they are designed to help increase English proficiency.
The average domestic annual cost of tuition at a US community college is $3,770, compared with $10,500 for public four-year colleges. The average age across community colleges is 28; and these institutions are much more diverse in their demographics than traditional four-year universities (i.e., in terms of age, race, educational background, goals, experience).
The most popular fields of study are business/marketing, health professions and related clinical sciences, computer and information sciences, liberal arts, and engineering technologies/technicians. However, there is a huge range of programs available at community colleges. Education USA notes that American community colleges lead the way in educating students in “biomedical technology, biotechnology, robotics, laser optics, internet and computer technologies, and geographic information systems.”
Community colleges are also known for the transferability of some of their programs – in other words, credits or an entire certificate or a degree from a community college often can be used toward a four-year degree at a college/university. These transfer agreements are most common between community colleges and universities that are geographically close to each other (e.g., the same city or same state). This is not true at all community colleges, and transferability may only apply between certain two-year community colleges and four-year colleges/universities. Understanding transfer arrangements is a key task of the agent placing international students at community colleges.
It is very important to clarify whether or not a community college program has a “2+2” transfer agreement with other four-year institutions before applying. This information is crucial for many students. At the same time, there are many four-year institutions that evaluate and accept community college credentials and students without 2+2 arrangements in place, so the lack of a 2+2 transfer agreement does not necessarily mean a community college student cannot progress to a four-year institution.
If you are considering studying in the us and need guidance, contact us for a free consultation.
Why consider attending a community college?
American community colleges offer several advantages for international students:
- Easier Transition and Support: Community colleges provide dedicated staff to help international students with cultural, language, and study challenges, offering an easier transition to the American education system .
- Open Admissions Criteria: They have lower admission requirements, allowing students with lower grades/test scores to enter degree programs and improve their academic performance for potential transfer to four-year institutions.
- English Language Support: Community colleges offer robust English-language upgrading courses, tutoring services, and may require lower TOEFL scores, making it easier for international students to begin their studies.
- Job-Ready Skills: They offer excellent associate degrees and certificates that provide job-ready and in-demand skills in the American and global economy.
- Cost-Effective Entry Point: Community colleges have lower tuition rates, making them a less expensive entry point into American higher education, which is crucial for self-funded international students.
- Path to Bachelor’s Degree: Many community colleges have transfer agreements with four-year colleges, offering a cost-effective path to obtaining a bachelor’s degree through “2+2” transfer programs.
- Guaranteed Admissions: Some four-year colleges and universities offer guaranteed admissions to graduates of community colleges with which they have transfer arrangements, providing a clear pathway to further education .
Overall, American community colleges offer a supportive environment, cost-effective education, and pathways to further academic and career success for international students.
Now that you have the basics of the American study system, you may want to take the step towards choosing the most adequate university in America or any other country in the world.
Carnegie Classification System
A useful tool for understanding the different types of higher education institution (HEI) that international students can attend in the US is the Carnegie Classification System:
- Doctoral universities: HEIs that awarded at least 20 research/scholarship degrees in the past year that are not professional practice doctoral-level degrees (such as the JD, MD, or PharmD).
- Master’s colleges and universities: HEIs that awarded at least 50 master’s-level degrees and fewer than 20 doctoral degrees during the past year.
- Baccalaureate colleges: HEIs where at least 50% of degrees were awarded in the past year at the bachelor’s level or higher, comprising fewer than 50 master’s degrees or 20 doctoral degrees. In other words, bachelor’s degrees are these institutions’ primary focus.
- Baccalaureate/associate’s colleges: HEIs that mostly award associate degrees but that also have at least one baccalaureate (four-year) degree program. Associate degrees must make up at least 50% of all degrees awarded in the past year.
- Associate’s colleges: HEIs at which the associate degree is the highest level of degree awarded to students.
- Special focus institutions: Institutions where a single field or set of fields (e.g., music, art) dominate the focus of the institution and degrees awarded are linked to this field. These include
- Faith-Related Institutions, Medical Schools & Centers, Other Health Professions Schools, Engineering Schools, Other Technology-Related Schools, Business & Management Schools, Arts, Music & Design Schools, and Law Schools. For more on such institutions, please click here.
- Tribal colleges: International students are not eligible to attend these colleges because they are reserved for Native (Indigenous) Americans.
As well as understanding the Carnegie Classification System, agents should also know that there are many excellent vocational programs in the US delivered through Career and Technical Education (CTE) schools and community colleges. This is increasingly important because research shows that there is growing interest among students across the world in shorter, practical programs.
The Credits System in US Higher Education
The US education system follows a credit system where the credits earned during the course are used to calculate the final result. For an undergraduate/bachelor’s degree, students typically require 3-5 credits per course, totaling around 120-130 credit hours for the whole degree. On the other hand, for a master’s course, it is 3-4 credits per course, amounting to approximately 30-64 credit hours for the whole degree.These credits are taken at the rate of 15 to 18 credits in the semester of the bachelor's or 4 to 6 credits in the semester for the master's and doctorate degrees.
In some cases, one course may consist of additional units related, for example, to intensive language courses which is especially true for international students requiring additional language support. This may case the credits to reach up to 12 additional units per curriculum for intensive language only. In addition, some laboratory materials may consist of one to four study credits.
The GPA or grade point average, which ranges from 0.0 to 4.0, is used to grade students based on marks obtained in each course and credits earned for that semester. Understanding the grading scale is crucial, as it ranges from 4.0 for an A grade to 0.0 for an F grade.
The academic calendar in the US is divided into three semesters (Fall, Spring, Summer) or four quarters (Fall, Winter, Spring, Summer) depending on the institution. For semester-based institutions, the first semester usually starting in September and ending in January, and the second semester beginning in February and ending in June. Summer semester is typically optional for most degrees. Understanding the academic calendar is essential for planning studies in the US
If you intend to study at American universities, you should know how to calculate the grade point average also known as GPA, which determines the average estimate of the grade calculations you will know after obtaining grades, and you better be aware of the following symbols and numbers to know how to understand your grades. A = 4.0-3.9 = Privileged High A = 3.8-3.5 = Privileged B + = 3.4-3.2 = Very Good High B = 3.1-2.9 = Very Good B- = 2.8-2.5 = Very Good Low C + = 2.4-2.2 = Good High C = 2.1-1.9 = Good C- = 1.8-1.5 = Good Low D + = 1.4-1.2 = Acceptable High D = 1.1-0.9 = Acceptable
The academic system in American universities is following a steady course of development year after year, eventually making graduates of American universities competent in the local and international labor market in various fields. The school year in America is divided into two semesters and in some universities, there are separate third semesters called summer separation. The first semester usually starts in September and ends in January, while the second semester begins in February and ends in June. Summer vacation or the Summer Semester shall be between those two periods. The academic system in American universities is continuously developing, aiming to produce graduates who are competitive in the local and international labor market.
Intensive English and Foundation Pathway Programs in USA

Preparatory and English-language-specific programs offered at schools and colleges across the US are known as Intensive English Programs (IEPs) and they are designed to support students with limited English proficiency in improving their English in a short period of time. It is the often the first entry point for international students in the US as students are brand new to American culture and often have only very basic communication skills in English. It is crucial to ensure students entering intensive English programs and pathway programs will be adequately supported.
In recent years, there have been close to 75,000 international students on active F-1 or M-1 visas in the US enrolled in intensive English programs (IEPs) in the US. More than half of international students enrolled in American IEPs intend to go on to other levels of study in the country. The top nationalities in US IEPs are Chinese, Saudi Arabian, Japanese, Brazilians, and South Koreans.
It is important to note that IEP students will require an F-1 visa to enter the country, and F-1 holders in an intensive English programs must receive a minimum of 18 hrs of instruction per week.
Students studying at an IEP can generally be categorized as follows:
- To improve their English to the point they can be accepted into a US higher education institution;
- To improve their English for a specific career goal (for example, needing English for a job or career advancement);
- To improve the English required for a specific field of study (e.g., law, business, or teaching English in their home country);
- To improve their English for fun and for the joy of being able to communicate in this highly important language.
There are two ways English language courses can be delivered:
- By a US college or university, on campus or off campus;
- By a private institution (sometimes in their own facilities, sometimes on a college or university campus).
Program lengths
- Short-term courses: Available throughout the year, short-term IEP courses are 4 weeks in duration.
- Quarter/semester courses: 10 to 15 weeks long, these courses are mostly delivered on college/university campuses. There are start dates available at different points of the year.
Types of IEPS
English USA, the largest organization specifically serving IEPs in the US, explains the types of available programs:
- General, intensive English programs: For students who want to improve their English reading, writing, listening, and speaking, and conversation skills.
- Exam preparation programs: These help students get ready for college entrance exams (TOEFL, TOEIC, IELTS), or earn certificates that will improve their career choices (e.g., Cambridge exams).
- Academic English programs: For students who want to improve their academic English and the learning techniques needed to succeed in American universities such as note-taking, discussion, academic reading and writing, and research.
- Business English programs: These teach English needed for a career in business, such as participating in meetings, negotiations, social skills, telephone skills, report writing, and more.
- Certificate Programs: Combination programs that teach English and deliver certificates in law, marketing, management, finance, or other careers.
- Teacher Training Programs: For learning or improving the English skills required for teaching English in a student’s home country. These programs teach advanced English, teaching methods, lesson planning, and more.
Depending on their English proficiency, students will be eligible for one of the following levels of English instruction, which will have sub-levels in them as well (e.g., Low Beginning and High Beginning). Sub-levels will differ according to the individual school.
- Beginning—This would include students with little to no knowledge of the English language and may stretch (via a sub-level) to students who can communicate using very simple sentences and who might understand a little conversational language.
- Intermediate—This level would be suitable for students who can participate in simple conversations, if with some mistakes; such students can understand most conversation if it is spoken slowly and clearly. At a higher Intermediate sub-level, students possess more command of English grammar and a basic vocabulary, and can understand a good deal of even rapid conversation.
- Advanced—This would be the right level for students who are comfortable in a wide variety of conversational circumstances and subjects, who have good overall comprehension despite still making some errors with the language. The most advanced sub-level within Advanced is for students who communicate very well and mostly accurately; such students can talk about a wide range of topics. This last level is to fine-tune already proficient English skills.
The IEP the student chooses will hold a placement test at the beginning of the course to determine the right level for the student’s grasp of English.
Before starting an IEP application, students need to determine the following requirements:
- Budget: There is a very big range when it comes to the cost of courses. Make sure to find out what is included in a course fee (books, materials, medical insurance, etc.) and what is not.
- Type of experience desired: There will be students who want to focus mainly on learning English and those that want a more “fun” experience, complete with recreational activities. Have two lists of options: one for those who want to focus mainly on learning English and one for those who are looking for recreational opportunities.
- Region preferred: As we outlined in Section 1, the US is very different according to what region one is studying in. English USA offers an interactive map to help students locate member schools in preferred regions.
- Future study: If students’ plans include undergraduate or graduate study in the US, then they may want to consider a program located on a university campus – maybe even at the university they hope to attend.
- Housing: Housing is a very important matter for international students considering an intensive English program – especially for those with very limited English proficiency. For such students, it is even more challenging to adjust to US culture without a basic command of English, so they may require a more supportive environment (such as a homestay living with a local family) or Student Residences on-campuses often offer student residences where students often share a unit and meals are offered in a dining hall. Other off-campus housing options are more suitable for mature students such as hotels or apartments where students can live more independently.
Progressing From an IEP to Academic Program
If the student’s goal is to proceed to a college or university program, it is essential to ask what arrangements are in place for transferring to the program after the student has completed the English program.
Many students in IEPs have been given Conditional Admission (also known as CLAs) from universities. Conditional admission is generally offered to students who have the academic records required to be admitted to a university but who have not yet achieved the English proficiency requirement.
Such students’ admission to the academic program will be “conditional” – in other words, they will need to meet the English proficiency requirement (and possibly other requirements as well) to receive a full admission offer. The requirements for full admission will be detailed in the Conditional Letter of Admission the student receives, and they may include a TOEFL or IELTS test score, GMAT, or GRE.
Conditional Admission requirements are very important for the agent and student to explore, and some countries will require the student to have a CLA before they leave for study abroad.
Pathway Programs in USA
In many cases, international students will need additional academic preparation in addition to English proficiency before beginning to study in the degree program for which they have received “conditional acceptance.” The US government notes: “All pathway programs must contain credit-bearing coursework that is transferrable to the curricular requirements of a certified degree program at the school.”
Admission teams for the degree program will indicate a pathway program (also sometime called bridge or foundation programs) that students can enroll in. These programs must be accredited by an accrediting agency recognized by the US Department of Education and must lead into an SEVP-certified degree program.
Pathway programs are especially useful for international students who want to study in the US, but don’t yet have the English language skills and/or academic requirements they need to enter US colleges and universities.” The US government adds: “The purpose of bridge programs is to help students who do not meet entrance requirements for a degree program of study. Bridge programs may contain course work covering the lacked requirements as well as academic course work required for meeting the graduation requirements of a separate degree program.”
These programs are available to students wishing to gain entry into undergraduate or graduate programs. Bridge programs are also important for international students who intended to moving from one educational system (that in the home country) to another, and from one culture to another. Often bridge programs provide post-secondary courses combined with language and cultural training.
Here are just some reasons pathway programs (as well as IEPs) are becoming more common in the US:
- The number of international students is growing in the US, and from parts of the world where English is not the mother tongue.
- In many parts of the world, students have attended schools with a very different teaching style than the US – they can be accustomed to memorization rather than creative problem solving, silent note-taking rather than active participation, and completely different attitudes to what constitutes plagiarism.
- Colleges and universities need international students who are as comfortable as possible in English and American university culture. This helps them harmonize their domestic students with their international ones. Often universities will offer international students a “conditional admission” where they have to complete a designated bridge program to secure their acceptance and be formally enrolled.
There is great variation in pathway programs, which can be delivered in several ways. More and more university-governed IEPs offer bridge or pathway programs that can lead to admission into the host institution. They are also available at private non-profit schools/programs, and from private companies (often multinational) working with colleges and universities to deliver programs customized to their schools’ needs.
American K12 Education System in Focus
In 2020, there were close to 60,000 international students in K-12 education in the US, more than 90% of whom were enrolled at the secondary school level (i.e., high school).
The nationalities most represented among international students at this school level are China (more than 40%), as well as South Korea, Japan, Germany, Vietnam, Spain, Italy, Brazil, Mexico, and Canada.
In the US, international students can only attend public schools at the Grade 9–12 level, but private K-12 schools can accept students from kindergarten through to Grade 12.
The majority of international secondary students in the US are on F-1 visas (68% in 2019) while about a third are on J-1 (exchange) visas. Most international students on J visas are from Europe, while most F-1 students are from Asia. In 2019, German, Spanish, and Italian students composed 44% of all J‐1 secondary student visas.
All K-12 schools in the US, public and private, must be registered with the Student and Exchange Visitor Program (SEVP) to be able to accept international students. Nearly 3,000 K-12 schools now accept international students.
The IIE reports that most international secondary students in the United States ultimately seek to enroll in higher education, and that,
“The experience of learning in U.S. classrooms, immersion in English-language instruction, and adjusting to U.S. life prior to higher education can ease the transition of international students moving from U.S. high schools to higher education.”
More than 90% of international students in the US for secondary school studies attend private high schools, and more than half of these students attend religiously affiliated schools. Private schools are the first choice for several reasons, including the fact that US law prevents international students on F-1 visas to study for more than one year at a public high school. Students can then transfer to a private high school if desired, but it is naturally easier to enroll in one school for the duration of studies.
Students are evaluated through the year on their performance and progress, and report cards are sent home to parents periodically through the year so they can see how their children are doing academically.
Grading scales differ from school to school, but the most common scale is A through F, where A is the highest level of performance and F is a failing grade based on a scale of 0–100 or a percentile.
Beginning in 11th grade, most students with intentions to go on to higher education take standardized tests: the SAT and ACT are the most common and students may take one or both. There are also SAT subject tests that some students decide to take to bolster their college applications.
At the end of high school, students receive a Grade Point Average (GPA), which is a cumulative average score derived from the sum of the student’s tests, exams, essays, projects, assignments, participation in class activities and group work, and attendance record. Students can also be ranked in their class according to their GPA.
K-12 public schools get most of their funding from state and local budgets, while the federal government provides about 10% of schools’ budgets in the form of grants, some of which is tied to their performance on standardized tests, via the federal No Child Left Behind act.
Individual states and local school districts control most of the decision-making at the K-12 level.
Different states vary in how they share educational decision-making with local school districts, but together they decide on what subjects will be taught, how they will be taught, which books will be used, the school calendar, supports for special students (e.g., learning or physically challenged), how students are evaluated, and graduation requirements for different grades.
Like private schools, public schools in the US are accredited and students should only attend accredited schools.
The class ratios are generally 18–25 children to one teacher. The teacher may also have the support of a teacher’s aide and/or a special education teacher (who helps with integrating developmentally or physically challenged children into the classroom).
Private K12 Schools
In the US, some families with abundant resources or financial aid choose to send their children to a private school to increase the chances their children will receive an excellent education. Many parents of international students also decide to send their children to an American private school, often with the hope that it will help to set them up for a place in a good American college or university.
There are roughly 35,000 private schools in the United States, serving more than 5 million students and enrolling about 10% of all pre-kindergarten to Grade 12 students in the country. More than three-quarters of students in private schools attend religiously affiliated schools. Almost 9 in 10 private schools have fewer than 300 students.
In some ways, there is more variety in the US K-12 private school system than in the public system, for the following reasons outlined by PrivateSchoolReview.com:
“While private schools are subject to all applicable local, state and federal laws and regulations governing the business side of things, private schools handle educational matters according to their educational philosophy and the wishes of their families and students. The essence of a private school is its curriculum and how it chooses to teach that curriculum is a matter which it decides in consultation with its clientele. The market drives private schools.”
The US Department of Education has this to say about US private schools:
- Private school students generally perform higher than their public-school counterparts on standardized achievement tests;
- Private high schools typically have more demanding graduation requirements than do public high schools;
- Private school graduates are more likely than their peers from public schools to have completed advanced-level courses in academic subject areas;
- Private school students are more likely than public school students to complete a bachelor’s or advanced degree by their mid-20s.
The National Center for Education Statistics’ National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) tests the knowledge and skills of the nation’s students in grades 4, 8, and 12. Routinely, the scores of students in private schools are much higher than the national average.
Many foreign-based families decide to send their children to private high schools in the US to prepare them for entrance to a US college, especially if the college is competitive and/or elite. A US World News Report lists these benefits for international students attending high school in the US:
- Improved English skills
- Easier navigation of the US college system
- College readiness
- Social skills
Many international students also take English-language courses during the summer break (i.e., outside of the normal academic year). The US government provides this guidance for visa rules and processes around summer language programs for K-12 students.
To attend a private school in the US, students must pay tuition. This is in large part linked to the fact that private schools are not funded by the government. This tuition can vary greatly, ranging from $10,000 to $40,000 to more for private boarding schools (which will be covered in an upcoming section). Beyond tuition, there will be additional fees as well which families must factor in to get to the true cost of a private school education. Financial aid for international students may be available at some private schools.
Private schools are able to charge so much tuition because of the extra resources, high quality of teachers, low student-teacher ratios, excellent facilities (e.g., sports, arts, computer), and extra-curricular opportunities they provide students.
Here is a link to a private school search for the US (and Canada).
Because space at private schools is often limited, not all students who apply will be admitted. The application process for private schools can take months. Find out from the schools your students’ families are considering how far in advance to begin, and what documents and other steps are required.
Boarding Schools in the US
BoardingSchools.us defines a boarding school as “a school where pupils reside during the semester.” They continue: “Students are provided with food and lodging in addition to their education, but a boarding school has much more than that to offer to students and their families. Traditionally, boarding schools provide an education based on small class sizes, high standards of academic excellence, and cultural diversity.”
At a boarding school, students live on the school’s premises as they study. Many boarding schools enrol both day students (who leave after school is done for the day to their houses) and “boarders” who stay on the premises for longer periods of time: Full-term boarders go home at the end of an academic year, semester boarders go home when the academic term is over, and weekly boarders go home for weekends. International students tend to be longer-term boarders rather than day or week students.
International students make up about 15% of all students in American boarding schools.
Teachers and staff sleep on the premises so they are quickly available to students at all times, even after school. Students receive all their meals from the school.
Most boarding schools charge tuition and fees for room and meals, and the typical cost ranges from $15,000 to over $65,000 per academic year. WorldScholarshipForum.com lists several scholarship programs for international students wanting to go to a boarding school.
Association of Boarding Schools (TABS) research has found that boarding school students are more likely to find academics to be challenging (91%) than private school students and public school students (71% and 50% respectively). Boarders tend to have more homework and more extra-curricular activities like sports and music.
They are often diverse: more than half of boarders reported that their school is “ethnically and racially diverse,” compared to 19% of private day students and 39% of public school students.
US K-12 boarding schools are very popular destinations among families overseas who want to see their children receive an excellent K-12 education and in many cases, progress to a quality American college or other post-secondary institution. Some families consider benefits of boarding schools to be:
- The personal development and confidence that comes from the challenge and adventure of living away from home with an eclectic mix of other students;
- The close friend networks that can be formed at boarding school can last a lifetime;
- Small school and class sizes and close interaction between teachers and students;
- Specialty programs available at many boarding schools (e.g., dance, filmmaking, visual arts).
TABS found that fully 87% of boarding school graduates said their school prepared them well academically for university life. By comparison, 39% of public school students and 71% of private day school students reported the same.
BoardingSchools.com lists four basic steps to applying to a boarding school in the US:
- Complete the application forms which the school has on its website.
- Complete the common application which you can find on the SSAT website.
- Complete the common application which you can find on the TABS website.
- Complete the paper application forms which you have either downloaded or received from the school.
They offer this tip for international students:
If you are an international student, read the requirements for international students on each school’s website. These requirements will differ from school to school, so do not assume that what one school asks for applies to other schools. You will have to take the TOEFL examination. Allow adequate time to prepare for and take this examination. The school will give you the documents which you need to apply for an F-1 visa. Apply for the visa as soon as you can. Some US consulates are booked months in advance for visa interviews. Bear that in mind as you apply to American schools.”
For a list of boarding schools in the US, please check this BoardingSchools.com link.
Now that you have the basics of the American study systems, you may want to take the step towards choosing the most adequate university in America or any other country in the world.
Submit an Inquiry
Entry Requirements in the USA for International Students

To study in the USA as a foreign student, there are specific entry requirements that need to be fulfilled. These requirements vary depending on the degree level and the university you wish to attend. Generally, international students are required to submit academic transcripts, standardized test scores (such as SAT or ACT for undergraduate programs, and GMAT or GRE for graduate programs), English proficiency test scores (TOEFL, IELTS, PTE Academic, or similar), an essay or statement of purpose, recommendation letters, Resume, a copy of a valid passport, and proof of finances. Specific degree requirements may also apply, such as high school transcripts for undergraduate programs or a bachelor’s degree with a minimum GPA for master’s programs. It is important to note that each university may have its own set of requirements, so it is essential to check the official university websites for detailed information.
To study in the USA as an international student, you will need to know what the student visa requirements are. The main visa category for academic study is the F-1 visa. To apply for an F-1 visa, you will generally need to provide the following documents: a valid passport, a Form I-20 issued by the education institution you plan to attend, financial documents to prove that you can cover tuition fees and living expenses, evidence of English language proficiency, academic transcripts and diplomas, and a completed visa application form (DS-160). Additionally, you may be required to undergo an interview at the U.S. embassy or consulate in your home country. It is important to check the specific requirements and procedures of the U.S. embassy or consulate in your country of residence, as they may vary.
Higher Education Requirements in USA

International education in the USA has advanced significantly since the mid-1950s, when enrollment of foreign students had only passed 35,000. International students make up around 5% of all students in higher education in the USA, and their numbers are increasing. More than 1,000,000 students from other countries have chosen to further their education and experience life in the USA, making it the country with the biggest population of international students in the entire globe. Study conditions in USA vary according to the nature of the academic specialization and the university in general. In this article, we shed light on study requirements for international students in USA.

Registration Application

In general, applications are accepted on the University's website, where the University offers all admission requirements for various disciplines. Some universities provide an online form to be filed by students with their personal data, specialization, certificates, degrees, medical examinations and so on. Some universities have requested that original copies or photocopies be sent in the courier.
Bank Statement

In most US universities and colleges, an application for an approved bank account is required when applying for a bank account indicating that there is enough credit in the student or his / her guardian to cover the expenses and installments of the school year. In the case of an external scholarship or scholarship through the state, the scholarship letter will be attached to the donor or the Ministry of Higher Education instead of the bank statement. In some cases, the student may have to send the approved bank account to obtain an admission from the university and then issue the scholarship letter from the donor or the Ministry of Higher Education based on the acceptance letter.
Objectives of Study Topic
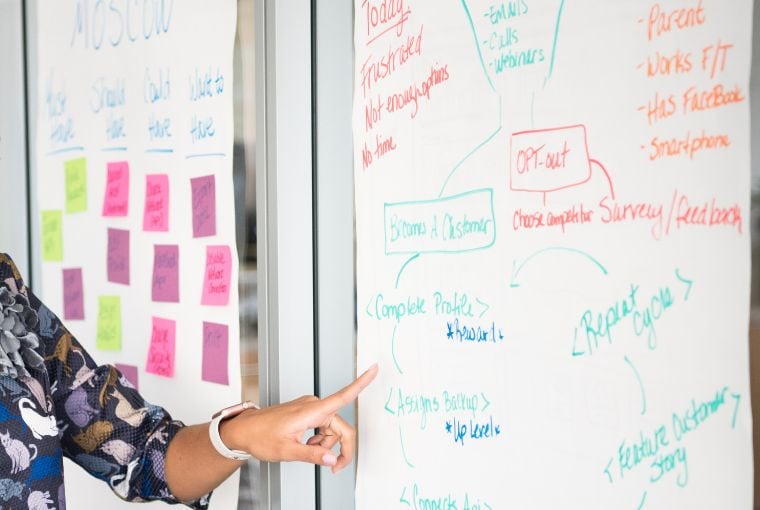

Some American universities, especially in the master's or in the required majors and higher studies, require the student to submit a structural topic explaining the reasons that made him wish to study that specialization in Tak University in America. Many universities rely on this message for screening students and distinguishing between their graphic abilities, cultural background, activities and others.
Admission Tests to Study in America

US universities are among the top 100 universities in the world. This is the most competitive universities in the world. In order to ensure the admission of the most distinguished students, admission to the university according to standardized and standardized admission tests will result in the student being admitted to the university In order to ensure the enrollment of outstanding students, it conducts tests for expatriates. Admission is determined according to the conditions of study in America and the grades obtained by the student in these tests. The most important of these tests are the following:
1. English Language Tests
The most important tests are IELTS and TOEFL. Most US universities require students to pass one of these tests within the required rate. If you do not get the required level, the student may enrol in an intensive language program before starting the academic program. Examinations of foreign schools may be exempt from these tests in their countries of recognized academic confessions. The required level of the IELTS test ranges between 5.5 and 6.0 for unconditional admission at the bachelor level and may reach 7.0 or 7.5 for the master's and doctorate studies. In terms of TOEFL, these rates range from 80 to 100.
2. Scholastic Assessment Test (SAT)
It is used in many American universities and some Canadian universities to enrol at the level of a bachelor's degree. This test measures the student's ability to address and solve problems, as well as math, reading, and academic skills.
3. American College Testing (ACT)
The test is quite similar to the SAT test and it is enriched but is also newer and is also used for admission to the undergraduate US universities. The test consists of 4 parts namely English, Mathematics, Social Studies and Natural Sciences.
4. Graduate Record Examinations (GRE)
The Students wishing to enrol in graduate programs in America are required to apply to many universities. This test measures English language skills, critical thinking, quantitative and analytical skills.
5. Graduate Management Business Admission Test (GMAT) Graduate Management Admission Test
The Students wishing to enrol in MBA programs are asked at many universities in the world. And this test assesses the analytical ability and ability to solve problems and data exploitation and logical thinking skills of applicants
6. Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)
This test is taken prior to the completion of a bachelor's degree in biology or chemistry or any speciality that qualifies for the study of human medicine. It consists of 4 sections in the chemical and physical principles of biology, the skills of critical and intellectual analysis, and the psychological, social and biological bases of behaviour.
7. Dental Admission Testing Program (DAT)
A standardized test under the supervision of the American Dental Association is taken by those wishing to study in America or Canada. The test consists of four sections: natural sciences, cognitive ability, quantitative thinking, and intellectual analysis.
8. Pharmacy College Admission Test (PCAT)
Testing for students wishing to enrol in the American College of Pharmacy consists of 5 sections: Writing, Biology, Chemistry, Analytical Reading, and Quantitative Thinking.
9. Law School Admission Testing Program (LSAT)
A basic test for admission to some law schools in America and Canada. The purpose of this test is to identify the student's chances of success in law school.
Applying to a Community College
Focus Questions:
- Is it possible a community college might have scholarships for which international students are eligible?
- Is it possible that an international student might work in the US for a period of time after graduating from a community college?
Unlike most four-year colleges and universities, many community colleges do not require international students to take standardized admissions tests to gain admission. Many require that they take an English proficiency test, and/or an English placement test upon arrival for proper course placement. In addition, many have rolling deadlines for admissions.
These are some of the other requirements they may have:
- Application fee
- Bank statement (check with individual college for required amount)
- High-school diploma or high-school equivalency, and possibly academic transcripts from all institutions ever attended
- TOEFL scores (check with individual college for required score) or other English-proficiency test scores
- Copy of passport
Application procedures, deadlines, and start dates will vary greatly among individual community colleges. In addition, there may be program-specific requirements.
In many cases, consultation with the individual community college will determine whether the student should apply first to an Intensive English Program (IEP) delivered within the school or straight into the certificate or degree program. This will depend on student goals as well as English proficiency.
There may be institution-specific scholarships available at some community colleges, staggered payment plans, and if an international student is doing well at a community college, they may go on to receive a scholarship at a four-year institution.
In general, international students should apply at least three months before the start of a degree or certificate program session and at least two months before the start of an IEP course.
Some international students may find on-campus jobs where they can work for up to 20 hours a week, but these are limited. In addition, students may apply for permission, while studying, to remain in the US for a year after they graduate to obtain work in their field of study.
Healthcare and Safety
Healthcare and safety are important considerations for international students studying in the USA. The country has a well-developed healthcare system, with access to advanced medical facilities and quality healthcare services. Many universities provide health insurance options for students, ensuring that they have coverage for medical expenses. Additionally, campus health centers are available to provide basic medical care and support.
In terms of safety, education institutions in the USA prioritize the well-being of their students and have campus security measures in place. Safety resources, such as emergency response systems and campus police, are readily available to ensure social security. International students need to familiarize themselves with safety protocols and resources provided by their university to ensure a safe and healthy experience while studying in the USA.
Requirements for International Students Attending High Schools in the US
International students who want to attend public high schools will apply either for an F-1 or J-1 visa. Both classes of visa restrict study at a public high school to one school year. (By contrast, there is no time constraint for K-12 students on F-1 visas studying at private K-12 schools in the US).
The Department of Homeland Security states that,
“F-1 students attending an SEVP-certified public secondary school must compensate U.S. taxpayers by paying the full, unsubsidized per capita cost of attending school for one year in that location. Payment of this cost and the I-901 SEVIS Fee must occur before the prospective student applies for an F-1 or M-1 visa.”
There is no exception to this rule.
J-1 students attending public high schools:
- Must be between the ages of 15 years and 18.5 years of age on their first day of school in the US.
- Must live with local homestay families.
- Must return to their home country at the end of the school year and are usually excluded from returning to the US on any kind of student visa for at least two years.
- Can apply only through a specially licensed US organization that can only place a limited number of students each year; getting accepted to this program is a very competitive process that must be started almost one year in advance.
- Do not pay for school tuition fees because the J-1 program is subsidized by the government to further cultural exchanges between the US and the student’s home country. The main costs are airfare and placement and monitoring fees that students will pay to the J-1 placement organization.
- Usually do not have a choice on which location or school they will attend.
- Cannot graduate or receive a high school diploma, regardless of the number of credits they have earned.
In addition:
The J-1 program application process is somewhat complicated and the rules are very strict. F-1 visa programs, on the other hand, require a much simpler application and fewer supporting documents. This allows students to begin the application process earlier, and get accepted to the school of their choice much sooner.
F-1 students attending public high schools:
- Can live with local homestay families or live with non-immigrant relatives in the US while they study.
- May continue, after their year at a public high school, to a private high school or begin their university education without having to change their visa status or return to their country.
- Must pay school tuition and room and boarding fees with their own family funds since F-1 programs are not sponsored by the US government.
- Can choose which state, city and school they would like to attend depending on their qualifications and space availability.
- May be able to graduate and receive a diploma from the high school they attend (if they are accepted to Grade 12 and have enough credits to graduate within one school year).
For more information on J-visas at the secondary school level, please visit this US State Department webpage. For F-visas at this level in the public system, please visit this webpage.
Rules and Application Procedures for International Students in Private US K12 School
International students wishing to study in the US at the K-12 level must attend a school that is certified by the Student and Exchange Visitor Program (SEVP). These are the only schools authorized to accept international students. You can use this page to make sure the school under consideration is certified.
Because space at private schools is often limited, not all students who apply will get in. The application process for private schools must start much earlier and can take months. Find out from the schools themselves how far in advance to begin, and what documents and other steps are required.
Most private schools, especially at the high-school level, will ask that prospective students take one or more standardized admissions tests. These might include the SSAT (Secondary School Admission Test), the ISEE (Independent School Entrance Examination), the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language), or the school’s own tests. Students should begin studying for these tests about six months before actually taking them. The tests are meant to ensure the school and accepted students are a good match, and to place students properly in classes and provide them with the right supports (for example, English-language help).
Please Note: acceptance into a SEVP-certified school is the first step in an international student’s process to study in the US – before applying for a student visa.
For more information on how international students should apply for a visa to attend either a private school or boarding school, this PrivateSchoolReview.com article is helpful.
Boarding Schools
BoardingSchools.us defines a boarding school as “a school where pupils reside during the semester.” They continue: “Students are provided with food and lodging in addition to their education, but a boarding school has much more than that to offer to students and their families. Traditionally, boarding schools provide an education based on small class sizes, high standards of academic excellence, and cultural diversity.”
At a boarding school, students live on the school’s premises as they study. Many boarding schools enrol both day students (who leave after school is done for the day to their houses) and “boarders” who stay on the premises for longer periods of time: Full-term boarders go home at the end of an academic year, semester boarders go home when the academic term is over, and weekly boarders go home for weekends. International students tend to be longer-term boarders rather than day or week students.
International students make up about 15% of all students in American boarding schools.
Teachers and staff sleep on the premises so they are quickly available to students at all times, even after school. Students receive all their meals from the school.
Most boarding schools charge tuition and fees for room and meals, and the typical cost ranges from $15,000 to over $65,000 per academic year. WorldScholarshipForum.com lists several scholarship programs for international students wanting to go to a boarding school.
Association of Boarding Schools (TABS) research has found that boarding school students are more likely to find academics to be challenging (91%) than private school students and public school students (71% and 50% respectively). Boarders tend to have more homework and more extra-curricular activities like sports and music.
They are often diverse: more than half of boarders reported that their school is “ethnically and racially diverse,” compared to 19% of private day students and 39% of public school students.
US K-12 boarding schools are very popular destinations among families overseas who want to see their children receive an excellent K-12 education and in many cases, progress to a quality American college or other post-secondary institution. Some families consider benefits of boarding schools to be:
- The personal development and confidence that comes from the challenge and adventure of living away from home with an eclectic mix of other students;
- The close friend networks that can be formed at boarding school can last a lifetime;
- Small school and class sizes and close interaction between teachers and students;
- Specialty programs available at many boarding schools (e.g., dance, filmmaking, visual arts).
TABS found that fully 87% of boarding school graduates said their school prepared them well academically for university life. By comparison, 39% of public school students and 71% of private day school students reported the same.
BoardingSchools.com lists four basic steps to applying to a boarding school in the US:
- Complete the application forms which the school has on its website.
- Complete the common application which you can find on the SSAT website.
- Complete the common application which you can find on the TABS website.
- Complete the paper application forms which you have either downloaded or received from the school.
They offer this tip for international students:
If you are an international student, read the requirements for international students on each school’s website. These requirements will differ from school to school, so do not assume that what one school asks for applies to other schools. You will have to take the TOEFL examination. Allow adequate time to prepare for and take this examination. The school will give you the documents which you need to apply for an F-1 visa. Apply for the visa as soon as you can. Some US consulates are booked months in advance for visa interviews. Bear that in mind as you apply to American schools.”
For a list of boarding schools in the US, please check this BoardingSchools.com link
Submit an Inquiry
Study Costs in USA

Costs of Studying and Living in USA
Conditions and costs of study and living in America vary considerably depending on the university's program, lifestyle and location. In general, the cost of studying abroad is divided into the following costs:
University Tuition Costs in US
The cost of study in US varies according to the state, university, specialization and nationality of the student. In general, universities and colleges in US are divided into private universities and government universities. Private universities in America are usually more expensive than state universities in terms of premiums. US universities are often more equipped and developed than private universities. In general, the cost of studying in America varies between US $ 10,000 per year for some universities and colleges to as little as US $ 50,000 per year for the most prestigious universities such as Harvard, Stanford and Yale (these figures for the academic year 2017-2018). The cost of these premiums is reduced to more than 50% if the student is a US citizen and from the same state as the university. If the student is from another state, he shall treat the foreign student in terms of premiums.
Housing costs in US
Housing costs vary depending on the state and the choices available to students. Some students prefer university accommodation, others prefer to live with an American family, and others prefer housing in particular. On the whole, the costs of each type are different, and the costs of housing in major cities such as Los Angeles or New York are different from those in smaller and more important cities. For example, if a student wishes to live separately in a Midwest state such as Ohio or Kentucky, the studio rents the room or individual apartment from $ 500 to $ 1,000. If the student wants to live with an American family, he or she will have to pay about $ 450- $ 650 per month on average and include some meals. If the student offers a residence permit at the university, this will be the most expensive option in terms of housing costs and even living expenses. The average cost of university housing is $ 400 per month. It does not cost the student daily transportation to reach the campus. The electricity, gas and internet bills are paid by the university directly.
Cost of living in US
As for the monthly cost of living, they vary from state to state as mentioned above, but this is the average cost list in most American cities. It is very similar to what it is in other rich countries. It is certainly easy to find consumer goods, basic necessities such as food and cheap household items to almost all men and women who reside in the United States. The average monthly cost of living for university students in the United States is $ 450-750 per month (not including tuition). As in most countries, the price of living is higher in large cities than in small cities. The cost of electricity varies between $ 60 and $ 100 per month, which is reduced and increased on the basis of your daily use of electricity. The gas bill costs between $ 100 and $ 150 per month. Internet bill costs about $ 50 per month for super speeds. The cost of water and garbage removal companies is about US $ 75 per month. Either for food and beverage costs in the United States, this is a list of some basic daily meals consumed: 500 grams of bone chicken breast 1 liter of whole milk is $ 0.89 12 eggs, a big $ 3.17 1 kg of tomatoes $ 4.01 500 grams of local cheese 1 kg of apples $ 3.34 1 kg of potatoes 1.60 countries L of Coca-Cola $ 1.91 Bread for two people for one day $ 2.13
Study Costs in the USA

Studying in the USA can be a significant financial investment, and international students need to consider the study costs involved. To start the application process some educational institutions require their students to pay application fees that are considered. Tuition fees vary depending on the institution and program, ranging from $10,000 to $60,000 per year for undergraduate degrees and varying amounts for graduate programs. In addition to tuition fees, students need to factor in living expenses, which can vary depending on the location and lifestyle. On average, international students might expect to pay between $10,000 to $20,000 per year for living costs, including accommodation, utilities, groceries, transportation, and other miscellaneous expenses. It is worth noting that these figures are indicative and can vary based on individual circumstances and choices. Scholarships and financial aid options are available to help offset the study costs, and students are encouraged to explore these opportunities to make their education more affordable.
Sports-based Scholarships for International Students
Sports play a significant role in the USA, and universities offer a wide variety of sports programs and opportunities for international students. The USA has a strong sports culture, with a focus on collegiate athletics. Many universities have competitive sports teams in various sports such as American football, basketball, soccer, tennis, and more. International students with exceptional athletic abilities may have the opportunity to receive sports-based scholarships. These scholarships are awarded to talented athletes who can contribute to the university’s sports teams. The scholarships can cover tuition fees, accommodation, and other expenses, providing international students with the opportunity to pursue their education while participating in competitive sports. It is important for international students interested in sports-based scholarships to research the specific requirements and application processes of each university and sports program.
Accommodation and Transportation
Student accommodation and transportation options in the United States are diverse and cater to different preferences and budgets. When it comes to living arrangements for students on-campus housing is a popular choice, offering convenience and a sense of community. Off-campus apartments and shared housing are also available, providing more independence and flexibility. Homestays with local families offer a unique cultural experience.
In terms of transportation, public transportation systems such as buses, trains, and subways are widely available in major cities, making it easy for students to navigate their surroundings. Many universities also provide shuttle services for students to travel between campus and nearby areas. Additionally, students can opt for biking or walking in areas with pedestrian-friendly infrastructure. International students need to research and plan their accommodation and transportation options to ensure a smooth transition and comfortable living experience.
In-Campus Accommodation
In-campus accommodation in the United States offers international students a convenient and immersive living experience. Many universities provide on-campus housing options, ranging from dormitories and residence halls to apartment-style residences. Living on campus allows students to be close to academic buildings, university libraries, and other campus facilities, fostering a sense of community and making it easier to participate in campus activities. On-campus accommodation often includes amenities such as study lounges, laundry facilities, and recreational spaces. It provides a supportive university life for students to connect with peers, engage in extracurricular activities, and fully experience campus life. The cost of on-campus accommodation varies depending on the university and the type of housing chosen. International students should apply for on-campus accommodation early, as availability may be limited.
Off-Campus Accommodation
Off-campus accommodation in the USA provides international students with alternative housing options outside of the university campus. Renting an apartment or sharing a house with other students or roommates is a popular choice. Off-campus accommodation offers more independence and flexibility in terms of location, amenities, and lifestyle. Students can choose to live closer to their university or in neighborhoods that suit their preferences. Rent prices vary depending on the city and the type of accommodation chosen. International students need to research the local rental market, understand lease agreements, and consider factors such as transportation, safety, and proximity to amenities when selecting off-campus housing. Many universities provide campus resources and assistance to help students find suitable off-campus accommodation options.
Transportation
In a vast country like the USA, Transportation options for international students are diverse and accessible. Public transportation systems, such as buses, trains, and subways, are widely available in major cities, making it convenient for students to navigate their surroundings and commute to and from campus. Many universities also provide shuttle services for students, connecting campus with nearby areas. Additionally, biking and walking are popular modes of transportation in areas with pedestrian-friendly infrastructure. International students may also choose to own or rent a car for greater flexibility, although it is important to familiarize oneself with local traffic laws and regulations. Overall, the USA offers a well-developed transportation network that allows international students to travel conveniently and explore their surroundings.
Submit and Inquiry
FAQS
Q: What makes the USA a top study destination for international students despite its high cost of living and tuition?
A: The USA offers prestigious universities with rigorous admission standards, diverse study opportunities, and experiences ranging from cosmopolitan cities to rural towns, ensuring a suitable environment for all preferences.
Q: How do US universities support international students and enhance their overall experience?
A: US universities provide extensive academic support, help with adapting to new environments, mentorship programs, social/cultural activities, and opportunities for practical skills development and career advancement, contributing to high student satisfaction and success.
Q: Why is the USA considered a global powerhouse in economic and technological advancements?
A: The USA has the world's largest economy with a GDP of over $21 trillion, diverse industries, and is home to prestigious technology companies like Apple, Google, and Microsoft. Its economic strength and technological innovation make it an ideal destination for international students seeking top-notch education and career opportunities.
Q: What job opportunities are available for international students in the USA, and how can they benefit from them?
A: International students can work up to 20 hours a week during studies and full-time during vacations. Opportunities include on-campus jobs, internships, and programs like Optional Practical Training (OPT), which offer valuable work experience, financial support, and potential pathways to permanent residence. Popular part-time jobs include library assistants, research assistants, and tutors, with hourly salaries ranging from $12 to $17.
What are the main differences between F-1 and J-1 visas for international students attending public high schools in the US?
A: F-1 visa holders must pay the full cost of tuition and can choose their school, while J-1 visa holders do not pay tuition, are placed by a licensed organization, and cannot select their school. Both visas limit study at public high schools to one year.
What are the general costs associated with studying and living in the USA for international students?
A: The costs of studying and living in the USA vary widely depending on the university, location, and lifestyle choices. University tuition can range from $10,000 to $50,000 per year, with private universities generally being more expensive. Housing costs also differ, with options like university housing, living with an American family, or renting an apartment. The monthly cost of living for students, excluding tuition, typically ranges from $450 to $750, with additional expenses for utilities and food. Living costs are higher in major cities like New York and Los Angeles compared to smaller cities.








